- Your cart is empty
- Continue Shopping
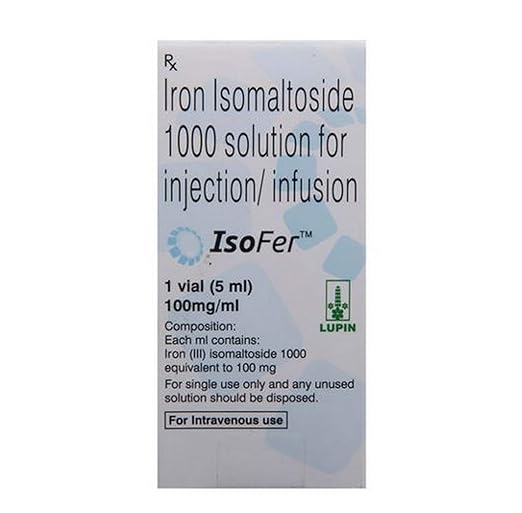
Isofer Injection is an iron supplement administered via injection to treat iron-deficiency anemia when oral iron is insufficient or not tolerated. Iron is essential for producing hemoglobin in red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout the body. Isofer Injection helps replenish iron stores quickly and effectively. It is given by a healthcare professional in a clinic or hospital and should never be self-administered. During treatment, patients are monitored for allergic reactions and effectiveness. Following a diet rich in iron, including meat, eggs, leafy greens, legumes, and fruits, can enhance the results of the therapy.
Uses of Isofer Injection
• Treats iron-deficiency anemia
• Provides rapid replenishment of iron stores
• Suitable when oral iron is not effective or causes side effects
• Supports recovery after blood loss or chronic illness
Benefits of Isofer Injection
• Restores depleted iron levels in the body
• Increases hemoglobin and red blood cell production
• Improves oxygen transport to tissues
• Reduces fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath
• Supports patients who cannot tolerate oral iron
• Helps achieve faster recovery in severe iron deficiency
Possible Side Effects of Isofer Injection
• Nausea or feeling sick
• Vomiting
• Diarrhea or loose stools
• Constipation
• Pain or swelling at the injection site
• Metallic taste or unusual taste in mouth
• Low blood pressure
• Redness or itching at injection site
• Dark-colored stools
How to Use Isofer Injection
• Administered only by a doctor or trained nurse
• Given as an injection or slow infusion in a clinical setting
• Dosage depends on severity of iron deficiency and patient condition
• Do not self-administer at home
• Follow the schedule and dose plan prescribed by your healthcare provider
How It Works
Isofer Injection delivers iron directly into the bloodstream. The iron is used by the bone marrow to produce hemoglobin in red blood cells. This enhances the oxygen-carrying capacity of blood, alleviating symptoms such as fatigue and weakness. Over time, normal iron levels are restored, improving energy and overall health.
What to Avoid
• Avoid if allergic to iron or similar injections
• Avoid using for anemia caused by factors other than iron deficiency
• Avoid use in conditions with iron overload
• Avoid taking oral iron supplements simultaneously without medical guidance
• Avoid rapid injection unless authorized
• Avoid use during severe infection unless prescribed
• Avoid in patients with uncontrolled liver disease
• Avoid alcohol consumption during treatment
• Avoid using expired or discolored medication
Safety Advice
Pregnancy – Use only if prescribed and deemed necessary by a doctor
Breastfeeding – Consult healthcare provider before use
Kidney Issues – Dose may require adjustment in kidney impairment
Liver Conditions – Use cautiously if liver problems exist
Allergy History – Inform your doctor about any past allergic reactions
Monitoring – Regular checks of iron and hemoglobin levels are recommended
Observe for Reactions – Watch for injection site pain, rash, or breathing difficulty
Driving & Tasks – Avoid driving if feeling dizzy or light-headed
Precautions
• Confirm iron deficiency with medical tests before treatment
• Inform doctor about all other medications and supplements
• Do not exceed recommended dose
• Monitor for signs of iron overload during multiple doses
• Avoid sudden posture changes after injection to prevent dizziness
• Maintain a balanced diet and stay hydrated
• Do not use expired vials or medication with visible changes
• Store in a cool, dry place protected from light
• Discontinue and seek medical attention if serious side effects occur









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.