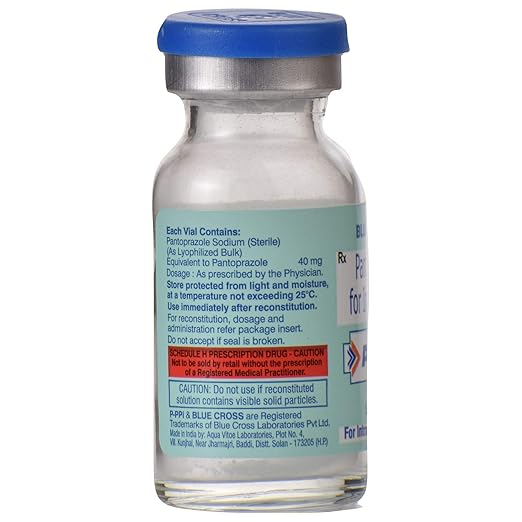
P-Ppi Injection is a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) used to reduce stomach acid. It treats acid-related conditions such as acid reflux, peptic ulcer disease, and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. It is also used to prevent stress ulcers in critically ill patients and is administered under professional supervision.
Benefits
-
Reduces excess stomach acid and relieves heartburn and indigestion
-
Promotes healing of peptic ulcers and prevents gastrointestinal complications
-
Prevents stress-related ulcers in seriously ill patients
-
Helps manage symptoms of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, and heartburn
Side Effects
-
Most side effects are mild and temporary
-
Common side effects include thrombophlebitis, dizziness, nausea, abdominal pain, flatulence, headache, vomiting, diarrhea, joint pain, and injection site reactions
-
Contact your doctor if side effects persist or worsen
How to Use
-
Administered by a doctor or nurse; do not self-inject
-
Dose and duration are decided by the healthcare professional based on your condition
-
Continue the full course even if symptoms improve
-
Lifestyle changes such as smaller, frequent meals and avoiding spicy, fatty, or caffeinated foods may improve results
How It Works
P-Ppi Injection works by blocking proton pumps in the stomach lining, which reduces acid production. Lower acid levels relieve symptoms, aid in ulcer healing, and prevent further acid-related complications.
Points to Avoid
-
Avoid alcohol, as it can increase stomach acid and worsen symptoms
-
Do not drive or operate machinery if feeling dizzy or sleepy
-
Avoid self-medication and skipping doses without consulting your doctor
Safety Advice and Precautions
-
Unsafe with alcohol consumption
-
Consult your doctor if pregnant, planning pregnancy, or breastfeeding
-
Use with caution in severe liver disease; dose adjustments may be required
-
Safe for patients with kidney disease, no dose adjustment generally needed
-
Inform your doctor of any history of liver disease, HIV medications, osteoporosis, or allergies to similar medicines
Missed Dose
-
If a dose is missed, consult your doctor; do not self-administer to make up the missed dose
Vendor Information
- Address:
- No ratings found yet!











































































































































Reviews
There are no reviews yet.